Should You Adjust Flow Control Valve Or Sprinkler Head
Managing Force per unit area in the Abode Irrigation System
By Kevin Moore, Justin Quetone Moss
- Jump To:
- Impact of Pressure on the Performance of an Irrigation System
- How does Irrigation System Design Impact Pressure?
- Addressing Problems Associated with Pressure
- How Much Water can I Save with a High Pressure System?
- Cost of a Force per unit area-regulated Irrigation System
The purpose of an irrigation system is to provide supplemental water to the landscape when rainfall is bereft. A system that is properly designed, installed and maintained will use h2o resource in a sustainable style. A critical component of irrigation efficiency is force per unit area management. Loftier pressure is oftentimes disregarded during pattern and installation. Low pressure may indicate a maintenance issue or damage to the system. This fact sheet will talk over pressure management as a tool for improving irrigation efficiency.
Force per unit area is defined as a forcefulness per unit area. You have probably checked the air pressure level in a tire and noticed that the gauge has units of psi, pounds per square inch. Residential water pressure level is ideally about twoscore to sixty psi, however, this can vary significantly based on location.
Bear on of Force per unit area on the Performance of an Irrigation Organization
If an irrigation system has depression water pressure, it causes a loss in irrigation efficiency. Some of the sprinkler heads may not pop up from the ground during operation. Water leaving a spray head or rotor volition not accomplish adjacent heads and the spray pattern volition not exist uniform. Brownish areas of the mural that are not receiving adequate h2o may be evident, leading you to run the irrigation arrangement longer. In some cases, there volition exist donut-shaped zones of brown grass around a sprinkler caput (Figure 1).
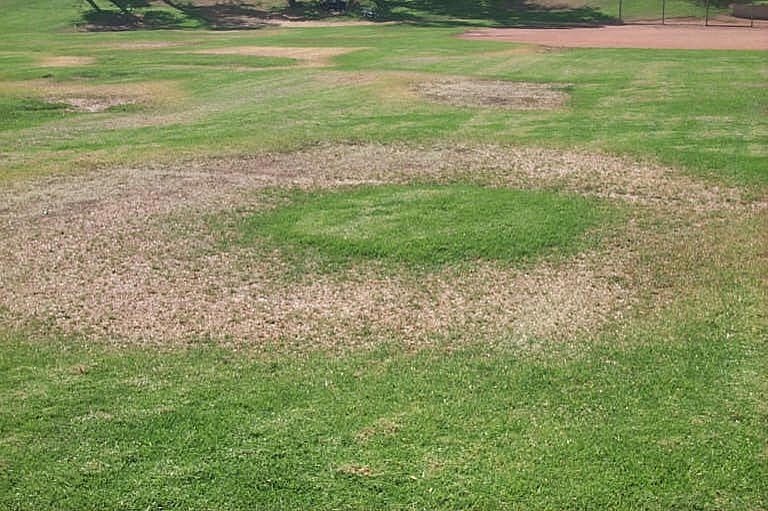

Figure i. Depression irrigation force per unit area tin can atomic number 82 to uneven irrigation patterns and poor plant wellness. Photograph courtesy of David Gerken.
Loftier water force per unit area causes a unlike set of problems. First is the potential of damage to the system. Merely similar too much air blown into a balloon, the components of an irrigation system can pause if the pressure becomes too high. This is most likely to occur where pipe is joined with a PVC fitting. The second trouble associated with high force per unit area is more common, a loss of irrigation efficiency. When the pressure level at a spray nozzle is besides high, the water leaves the nozzle as a fine mist instead of large aerosol. Carried away past the current of air, the fine mist evaporates before reaching the landscape. If a mist is seen around spray heads, high water pressure is probable (Figures 2a and 2b). High pressure also increases the menstruum rate of irrigation equipment (Figure iii). If the force per unit area moves outside of the design range for the device, then the awarding uniformity tin decrease drastically. For example, assume a sprinkler is operating at an optimum pressure of 30 pounds per foursquare inch (psi). The spray is evenly distributed within the arc and the flowrate is 3.3 gallons per infinitesimal (GPM) (Effigy 4a). Now, presume the pressure of that same sprinkler is increased to fifty psi, which is in a higher place the recommended operating range. The spray is no longer a uniform blueprint and the flow rate has increased to 4.8 GPM (Figure 4b).
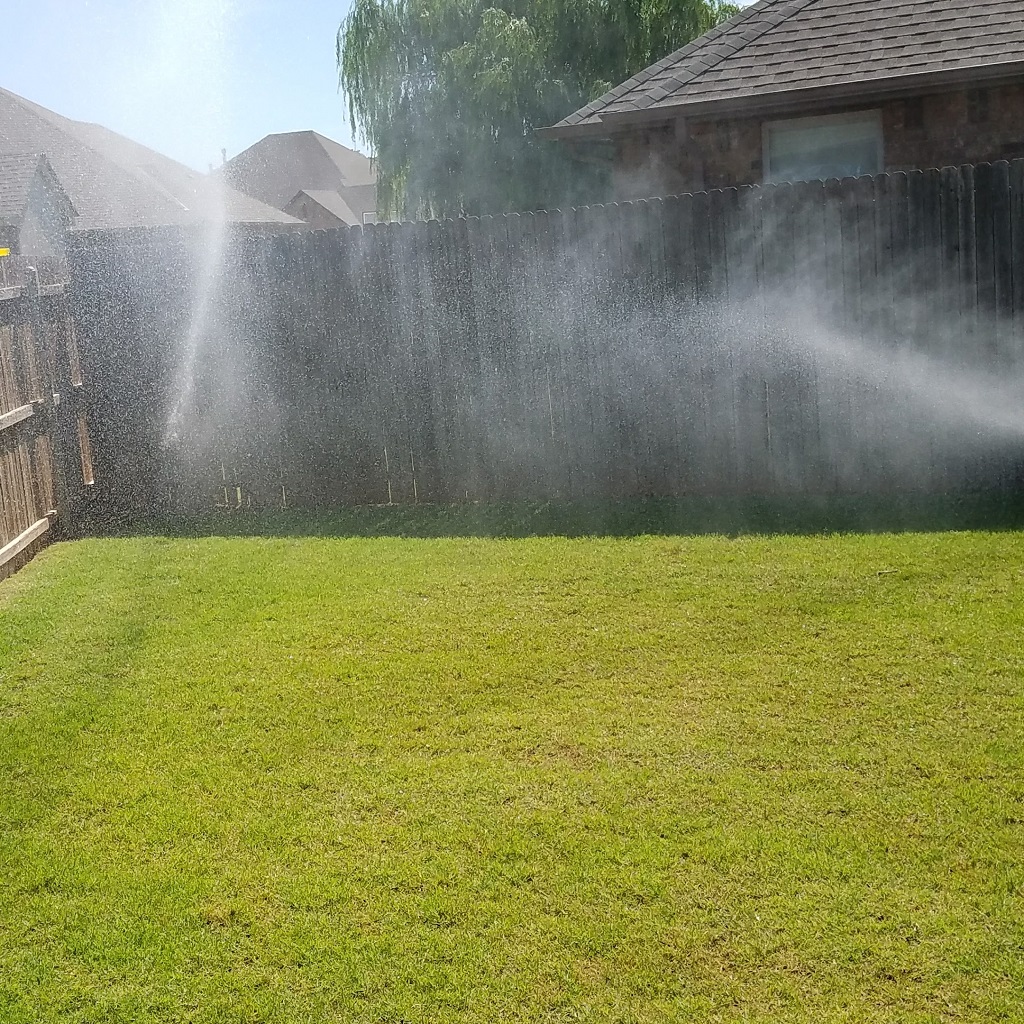
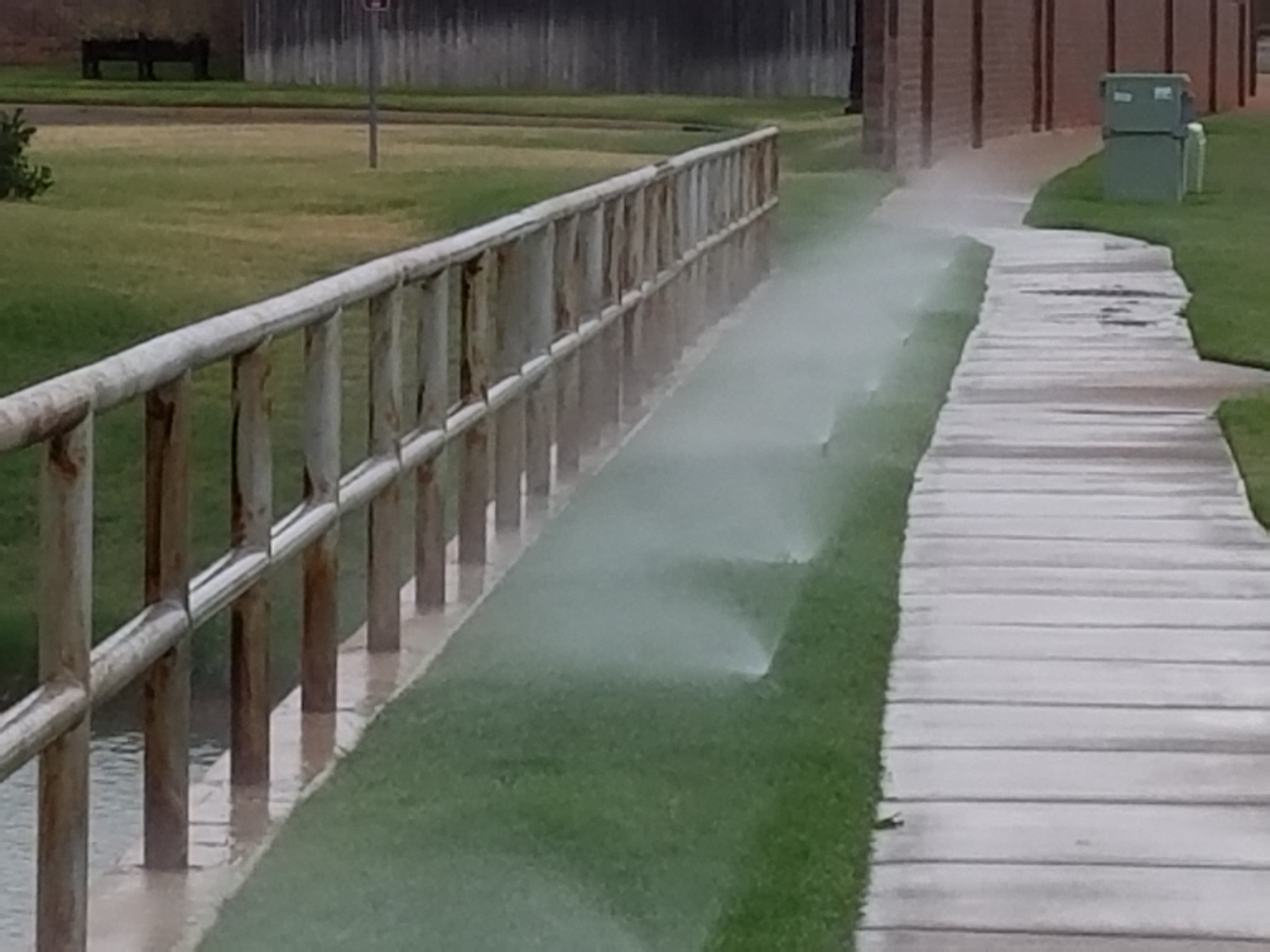


Figures 2a and 2b. High pressure in an irrigation organization leads to misting and a reduction in irrigation efficiency. Photos courtesy of Oklahoma Metropolis Utilities Department.
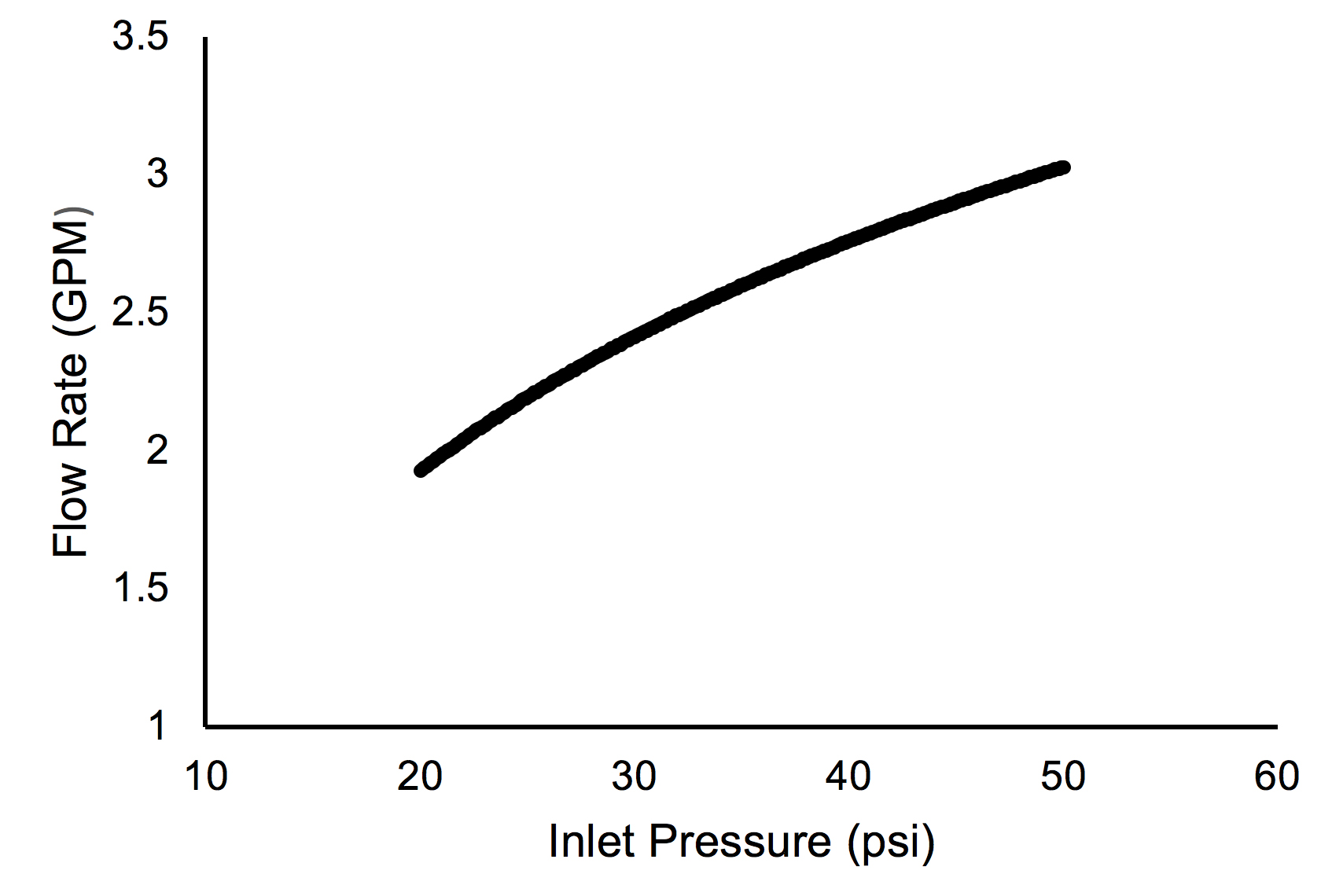
Effigy three. Typical human relationship of pressure versus flow rate. As pressure level increases, the flow of water from a single irrigation head likewise increases.
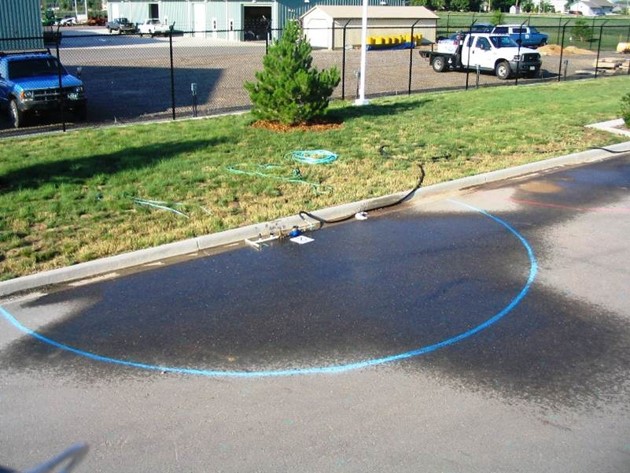
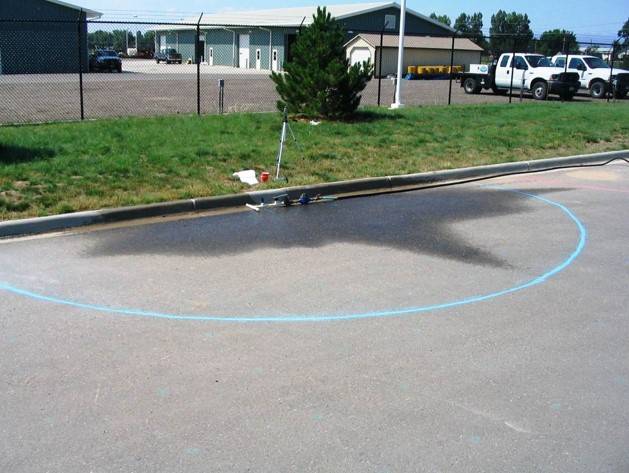


Figures 4a and 4b. At an optimum pressure level of 30 psi (top) the spray pattern is evenly distributed. When the pressure is increased to l psi (bottom) the spray design degrades while the menstruum charge per unit increases. Photos courtesy of Brent Mecham, Irrigation Association.
How does Irrigation System Design Bear upon Pressure level?
An irrigation organisation is made up of several components, and nearly all of these can affect the system pressure. Consider a typical residential irrigation system and its components (Figure 5). At that place are five main parts in a arrangement that movement water throughout the landscape: water meter, backflow preventer, command valves, mainline and lateral lines. Each of these has a pressure loss due to the friction associated with flowing h2o. An easy fashion to call up these pressure level losses is by using the 5-four-3-2-i rule of pollex, which indicates the pressure loss in psi from each of these 5 main irrigation system components (Table 1). Based on this data, expect a total pressure level driblet of about 15 psi (5 + 4 + 3 + two + 1) from the utility supply line to one of the sprinkler heads. If the utility is delivering water to your house at a pressure of lx psi, then expect a pressure of about 45 psi at each head. Still, the design of each specific irrigation arrangement can cause this pressure to exist higher or lower.
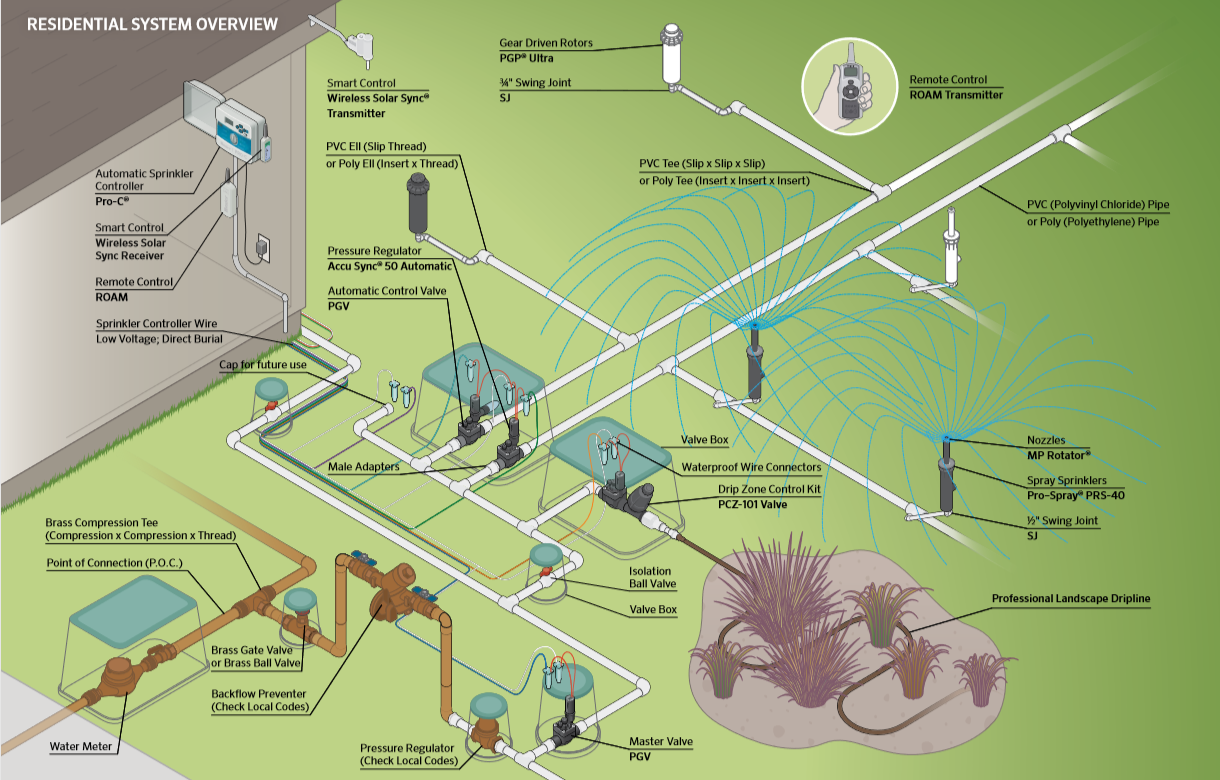 Effigy 5. Typical components in an irrigation system. Illustration courtesy of Hunter Industries.
Effigy 5. Typical components in an irrigation system. Illustration courtesy of Hunter Industries.
Unlike types of irrigation equipment take dissimilar ideal operating pressures for maximum efficiency. For rotors, this is virtually 45 psi, with an operating range of 25 to 65 psi. For spray heads, information technology is 30 psi, with an operating range of fifteen to 30 psi. For drip lines, this is almost xx psi, with an operating range of fifteen to 30 psi. Retrieve, flow rate and pressure are directly related to one another. If pressure is not well-controlled, irrigation efficiency will endure.
Addressing Problems Associated with Pressure level
If you suspect irrigation problems are associated with force per unit area, and then a good first step is to measure the water force per unit area at one of the hose bibs on your business firm. This does not account for pressure losses within the irrigation system itself, just it tin provide a rough idea of how much pressure level is existence delivered to the arrangement. Measure the force per unit area at the aforementioned time of day the irrigation system runs, as pressure can vary throughout the twenty-four hours. A pressure level gauge can be purchased for $10 to $20 online or at a local hardware store. Some of these will thread direct to the hose bib, while others will crave an adapter. If a pressure of less than 25 psi or greater than 125 psi is measured, contact the utility section for further investigation.
If dwelling pressure appears to be adequate, merely the irrigation pressure seems low, check the following items.
- Verify the isolation valve for your irrigation system is completely open. This should be located in a dark-green valve box somewhere between the water meter and backflow prevention device (Figures 6a and 6b). Sometimes the valve box can get covered with grass. Probing the grass with a screwdriver may aid locate the chapeau.
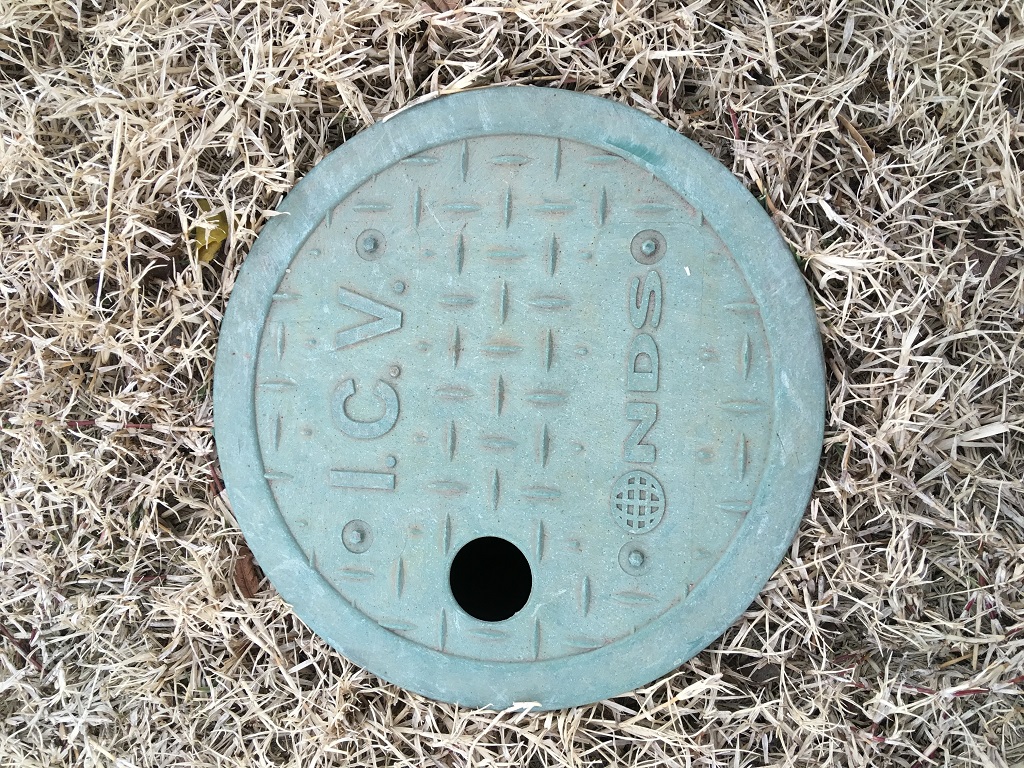
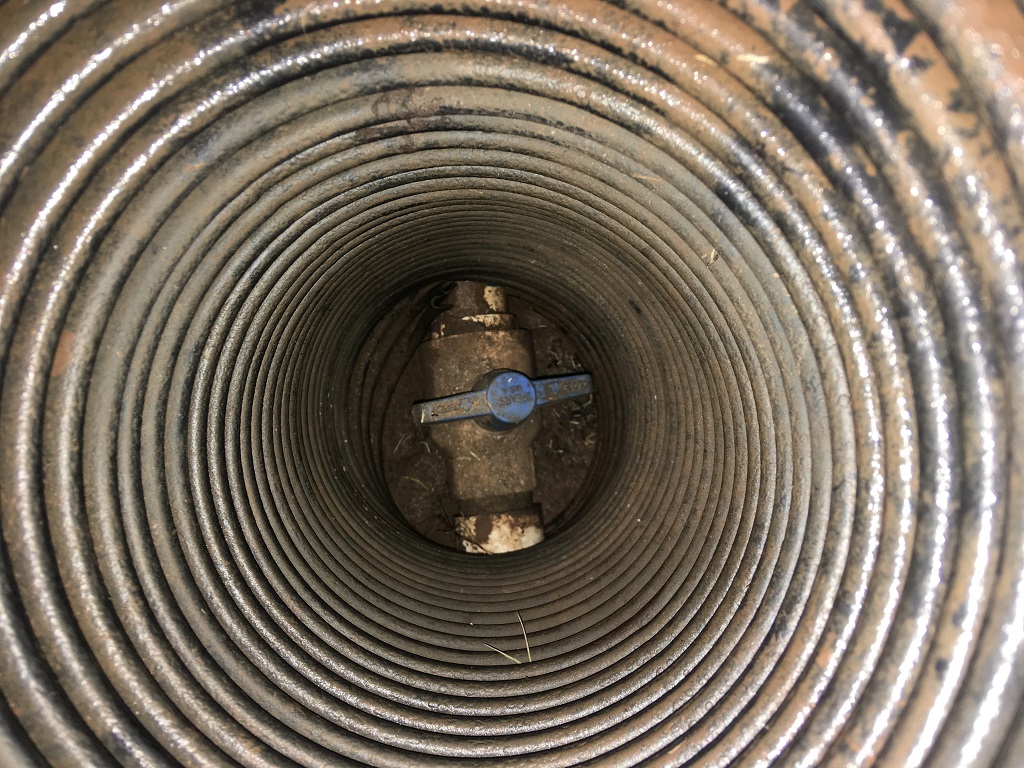


Figures 6a and 6b. The isolation valve is typically located in a small green valve box near the water meter or backflow preventer. This valve is in the airtight position. Photos courtesy of Kevin Moore.
- Verify the valves are completely open up on the backflow device. There are several different styles bachelor, but the pressure vacuum breaker (PVB) and reduced pressure principle associates (RPA) are common in Oklahoma (Figures 7a and 7b). Backflow devices are typically located outside, but may exist found in the garage in newer homes.
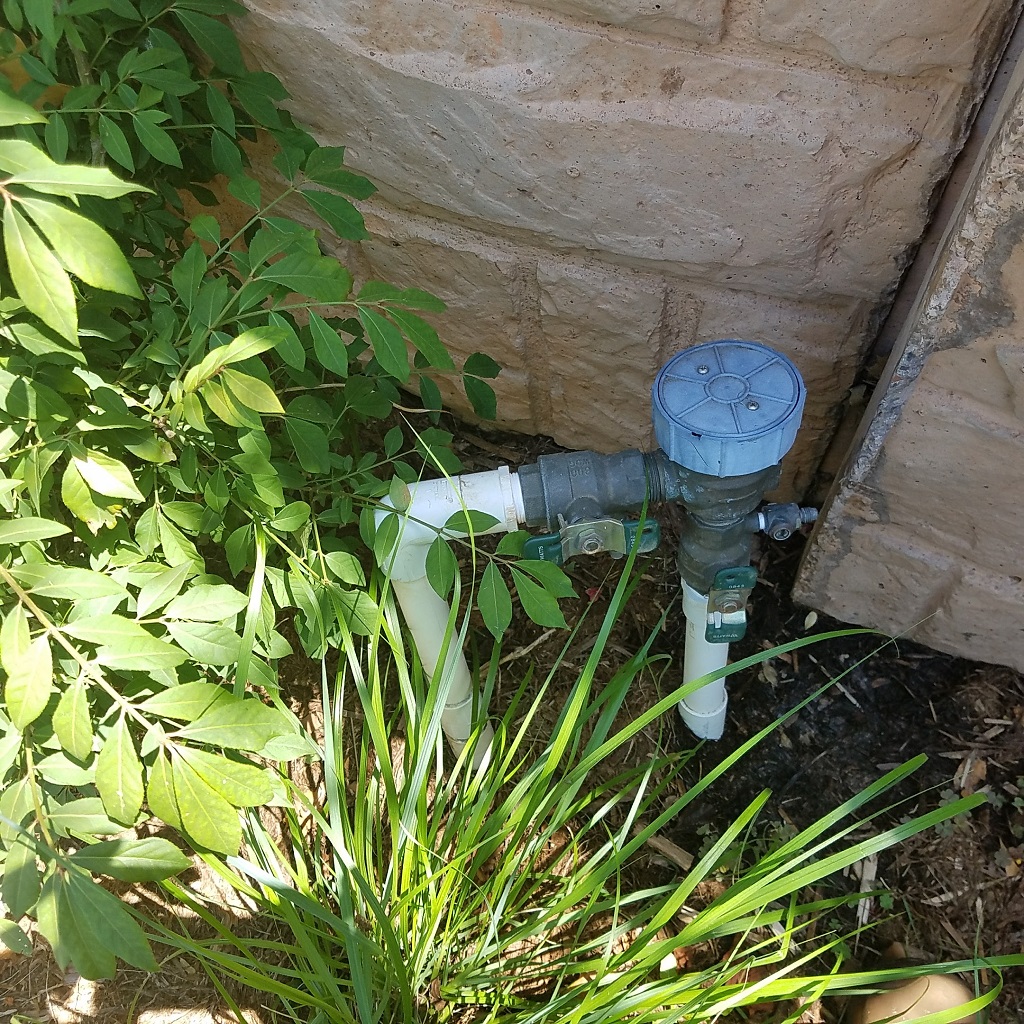
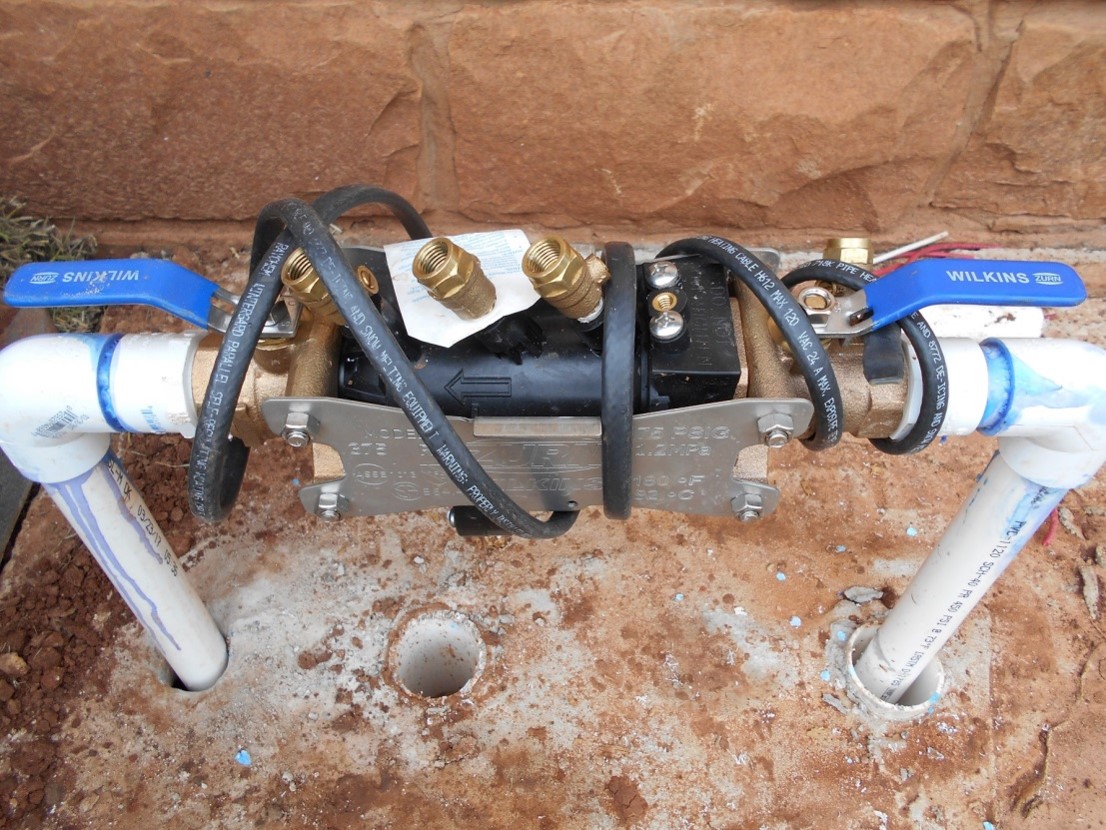


Figures 7a and 7b. Backflow preventers are designed to keep irrigation h2o from flowing back into the pipes used for drinking water. A pressure vacuum billow (top) and a reduced pressure level principle associates (bottom) are ii common backflow devices in Oklahoma. Note that both of the green- or blue-handled valves are aligned with the pipe. This is the fully open up position. Photos courtesy of Robert Reaves - Audit the backyard for any obvious water leaks. Since the piping is buried underground, look for soggy locations that never seem to dry out, or lush patches of grass in an otherwise dry location.
- Turn on the irrigation system and look for cleaved heads. This could be an obvious fountain of water coming from one of the heads or a stream of water coming from the base of operations about the basis. Make repairs as needed.
- Information technology is possible that the organisation was installed with undersized pipage and too many sprinkler heads on a zone. Low pressure tin be addressed past changing to lower menstruum nozzles or decreasing the number of heads in the zone. Contact an irrigation contractor for help in evaluating your arrangement.
The pressure associated with a fluid at rest is referred to every bit static pressure level. When a fluid is in motion – like when it flows through a piping – the pressure level volition drop forth the length of the pipe due to friction. The pressure level of a moving fluid is referred to every bit dynamic force per unit area.
If the irrigation pressure is high, there are several means to solve the problem.
- Install a pressure regulation device for the entire firm. If the pressure level is more than 80 psi to the firm, then consider this pick to protect the plumbing and appliances within your habitation. Contact a licensed plumber for this projection.
- Install a pressure regulation device at the irrigation organization point of connection. This is the same type of device used for the entire house, merely in that location may be circumstances when y'all would only need pressure regulation for the irrigation system. Contact a licensed plumber for this project.
- Regulate the pressure at the control valve for each zone. If you have a newer irrigation system, and then yous can probably install a pressure-reducing device directly on the control valve. A pressure reduction of at least 15 psi is required for these devices to part properly. One of these volition be required for each zone in the system. A local irrigation parts supplier should be able to help determine if pressure regulation can exist added to your existing control valves. These are typically located in a rectangular valve box with a green lid (Figures 8a and 8b). Remove the lid and attempt to identify the brand and model of valve that is installed in your system. If this is hard due to the age or position of the valve, take a motion picture with you to the parts supplier. They may exist able to identify the valve based on the photo. An irrigation contractor too can help to place the type of equipment currently installed.
- Regulate pressure at the head. Most irrigation equipment manufacturers sell pressure-reducing spray heads and rotors that will reduce the pressure at each device to the optimum operating pressure. This is a relatively straightforward modification that can be made by the homeowner, but requires the replacement of the spray body internals for every head in the system. Some homeowners will brand this modification over time on a zone-past-zone footing.


Figures 8a and 8b: Zone command valves
are typically located inside a green, rectangular valve box. There can exist several of these depending on the size of your system. Photos courtesy of Kevin Moore.
How Much Water tin I Salvage with a Loftier Force per unit area System?
Information technology is adequately common to find high irrigation system pressures throughout Oklahoma communities. Oklahoma Country University partnered with the City of Oklahoma Urban center, Oklahoma City Cute and Urban Backyard and Landscape to retrofit the equipment in several median strips to demonstrate potential water savings associated with pressure regulation (Figure nine). In one case, the boilerplate force per unit area at the spray head prior to the retrofit was 60 psi. A full of 157 spray heads were replaced with pressure-regulated spray heads, designed to reduce the force per unit area at the nozzle to 30 psi. Based on manufacturer data, the full output of the system at 60 psi was 215 gallons per infinitesimal (GPM). At 30 psi, the output was reduced to 153 GPM. This is a difference of 62 GPM (Effigy x). The irrigation system was operated on an odd- or even-twenty-four hours schedule for xviii minutes each run. For a typical summertime month, this pressure reduction should provide a savings of 16,740 gallons of water! This is the equivalent of 973 showers for a typical American. In addition to the water savings, less mist was generated during operation. This means that more of the water made it to the soil, where it could be used past the grass and mural plants, and less water was carried into the street by the wind. A typical residential system contains about 40 spray heads and water savings are probably closer to iv,000 to 5,000 gallons per month. This is a expert case of how a lilliputian work can go a long style toward improving the efficiency of an irrigation system and conserving a valuable resources.
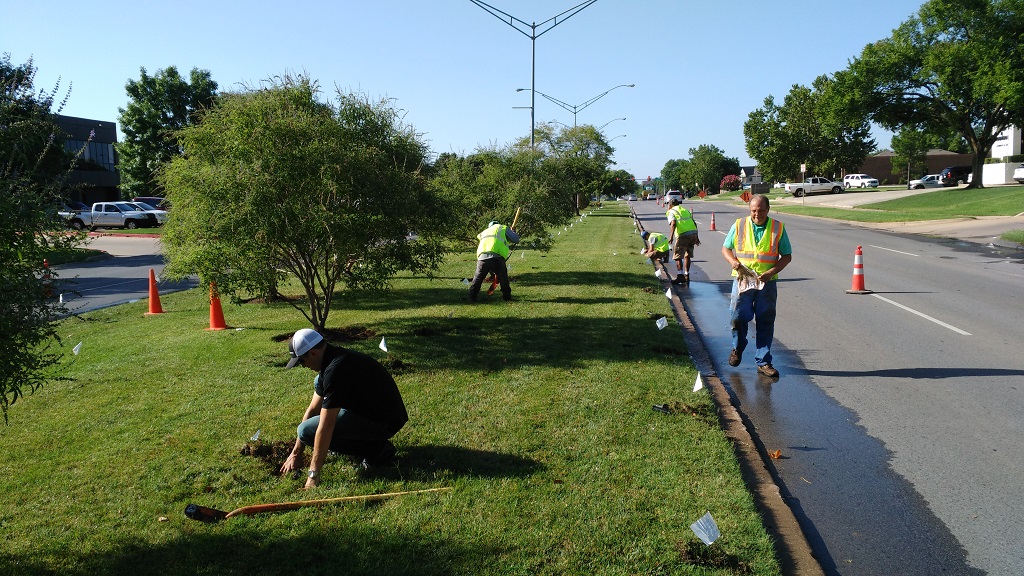

Effigy 9. Oklahoma City median retrofit project on Northward Classen Boulevard. Photograph courtesy of Joshua Campbell.
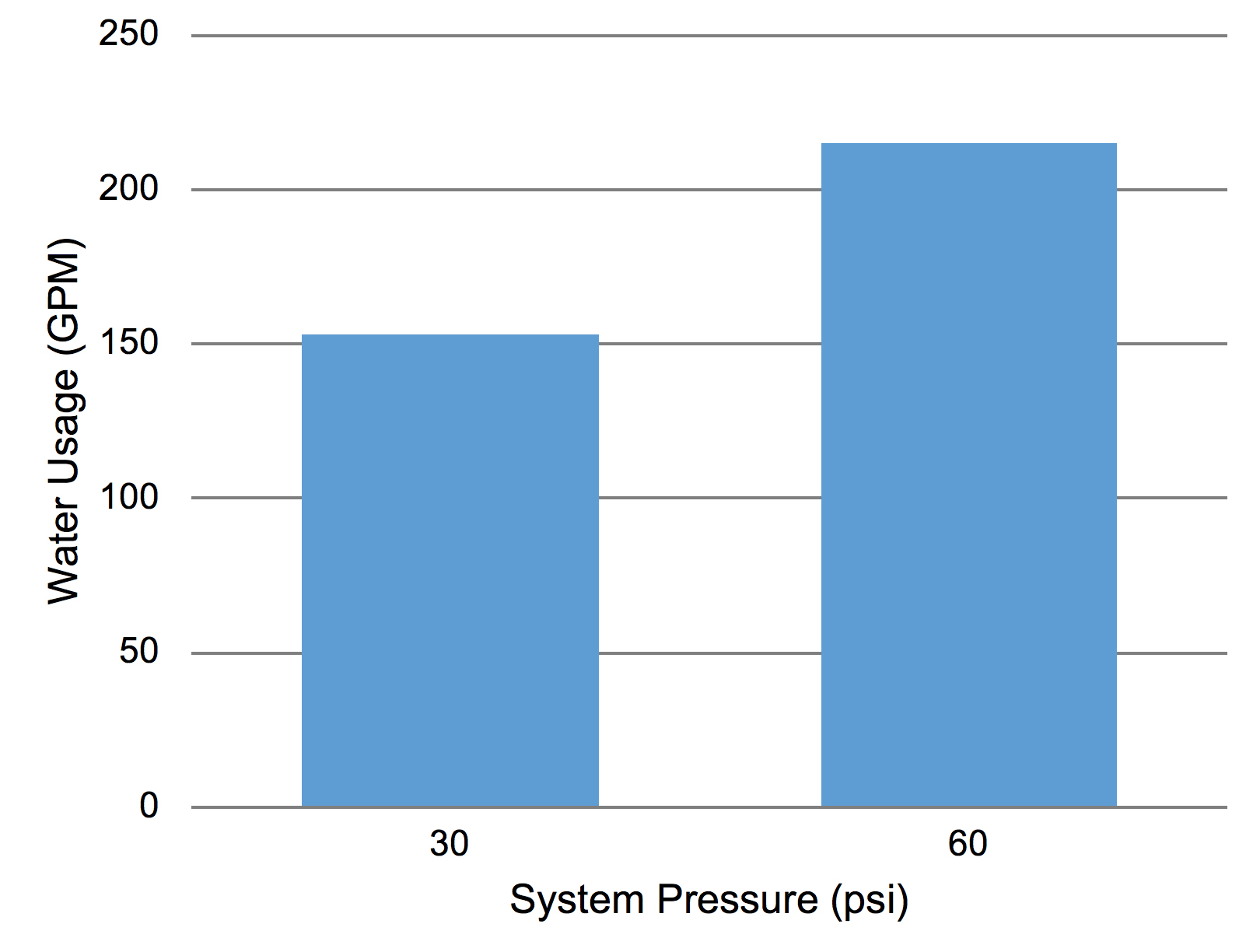
Figure x. Based on manufacturer data, the installation of pressure-reducing spray heads reduced h2o consumption past nearly 30 percent during one of the median retrofit projects in Oklahoma Urban center.
Cost of a Pressure level-regulated Irrigation System
The toll departure betwixt standard sprays and rotors and their pressure-regulated counterparts is only a few dollars. Labor price from the installation of pressure-regulated heads is identical to installation of standard heads. If you have high water pressure, and so force per unit area-regulated heads or devices should always exist used. The return on investment (ROI) when water pressure and water rates are high is typically one yr or less. From then on, the homeowner has an irrigation system operating at optimum pressure, both saving money and applying water more uniformly to the landscape.
For boosted data about maintaining the performance of an irrigation arrangement, delight refer to the following fact sheets.
HLA-6610 Uncomplicated Irrigation Audit for Home Lawns in Oklahoma
HLA-6615 Unproblematic Irrigation Checkup for Domicile Sprinkler Systems
Kevin Moore, PhD
Extension Acquaintance
Justin Quetone Moss, PhD
Research and Extension Specialist
Was this data helpful?
YESNO
Should You Adjust Flow Control Valve Or Sprinkler Head,
Source: https://extension.okstate.edu/fact-sheets/managing-pressure-in-the-home-irrigation-system.html
Posted by: andersonparpookin1962.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Should You Adjust Flow Control Valve Or Sprinkler Head"
Post a Comment